

A study by Hussein Abu-Rayyash, Shatha Alhawamdeh, and Yuri Ringomon, titled The Eye-Ear Relationship: Investigating Auditory Impacts on Subtitle Reading and Comprehension (2024) explored how subtitles affect language learning and comprehension. The study used RealEye eye-tracking system to gather detailed data on participants’ eye movements as they engaged with subtitled content in different languages and auditory conditions.
RealEye was instrumental in capturing the interactions between participants and subtitles. The analysis considered measures such as average fixation duration, total number of fixations, saccade length, and percentage of skipped subtitles, to measure how viewers processed visual information under different conditions. These metrics revealed patterns like increased fixation time when audio was absent, showing the cognitive demands of relying solely on subtitles. The data also highlighted differences in how Spanish and Arabic subtitles were read, providing insights into the cognitive challenges associated with processing different languages.
The study revealed several notable insights about how audio and subtitle combinations impact learning:
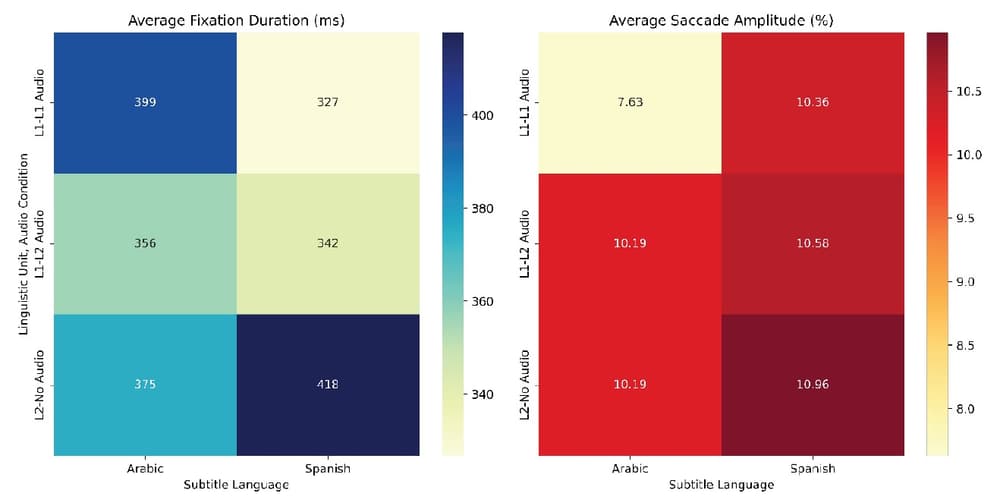
This study highlights the complex relationship between audio, subtitles, and language learning. The use of RealEye allowed researchers to analyze these dynamics in detail, providing valuable insights into how learners process subtitled content. These findings could help improve the use of audiovisual media as a language learning tool and inform the design of more effective subtitling strategies.

The authors of the study contacted RealEye to share their excitement about incorporating the platform into their research. They emphasized that RealEye was instrumental in making their work possible, allowing them to investigate how subtitles are read and understood under different auditory conditions.
The authors expressed their appreciation for RealEye’s accessibility and its ability to support innovative research outside traditional lab environments.


Follow the steps below to start your own experiment with RealEye:

Ready to set up your own study? Visit RealEye Support page to learn more and keep us posted on your results! 🚀